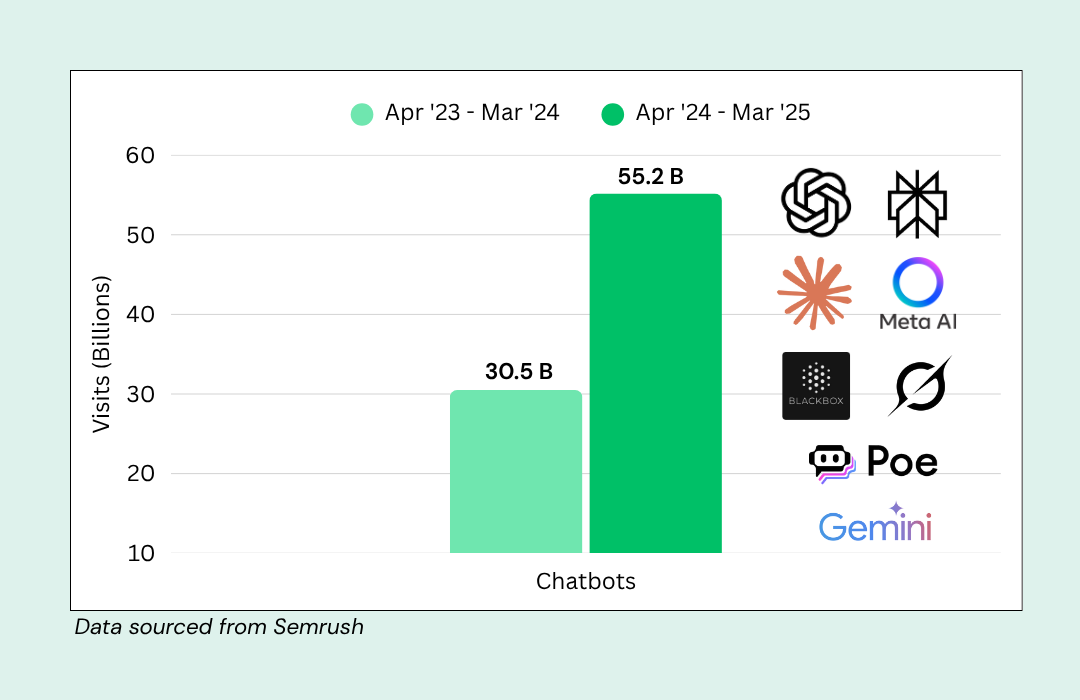
Before we dive into sales cycle management, let’s first focus on what a sales cycle is and the sales cycle steps.
What Is a Sales Cycle?
A sales cycle is a term used to describe the sales process steps, beginning when a sales rep identifies a potential customer to follow up after closing the sale. To put it simply, a sales cycle is the journey a potential client embarks on that begins when they develop an interest in a product to when they make a purchase.
And why is it important?
Understanding your sales cycle is critical to your success because:
- It helps you keep track of all sales, including how many steps each sales rep went through.
- It gives you insight into your sales processes and allows you to evaluate their effectiveness.
- You can adjust and make necessary improvements to their sales process.
What Are the Seven Steps of the Sales Process?
Here, we summarize the sales process stages. Be sure to understand the context in which you apply these in your overall sales lifecycle.
1. Prospecting
This process involves identifying potential clients who might be interested in your product or service. It’s considered the foundation of every sales process. Sales prospecting is to find qualified leads that are close to being ready to buy the advertised business or service.
Companies start prospecting by formulating an Ideal Customer Profile. An ICP is a summary of the perfect client for a company’s product/service. It focuses on the sales and marketing teams and helps gain important insight such as customer needs.
So not only do sales reps prospect for new customers, but they also qualify them. Prospecting often involves creating awareness to potential customers. Sales representatives can achieve this by advertising their product/service on social media sites such as Facebook and Instagram, blogs, and even podcasts.
2. Preparation
The second step in the sales cycle stages is preparation. It entails carrying out research and gathering vital information regarding your customer so that you can make a good pitch guaranteed to close the deal.
It’s important that sales teams familiarize themselves with information about the prospects such as needs, wants, expectations, and relevant background information such as occupation and education.
This information will help you when coming up with the perfect sales pitch that will appeal to your prospect and sell the value of whatever product/ service you might offer.
3. Approach
This is where you make or break your first impression. In this stage of the selling cycles, sales teams get to meet the client, either in person or through video conferencing apps or even email. Here, sales reps introduce themselves and set out to create a rapport with the prospect through small talk, asking questions, and other conversational skills.
4. Presentation
In the presentation stage, sales teams demonstrate how their product or service directly meets the prospect’s needs. The presentation should be tailored to identify and address the prospect’s pain points and offer a solution.
Sales teams may use PowerPoint or Keynote presentations to explain their points more clearly and may also offer interactive sessions where the prospect tests the product. Cross-selling and up-selling are sometimes used during this stage.
5. Handling objections
Sometimes the customer may have some concerns or hesitate before buying your product. It’s natural to require more information before making a decision. Good salespeople should consider these objections as leeway to further understand the prospect’s needs and adjust to them.
Below are a few tips that might come in handy when faced with objections during a sales lifecycle:
- Acknowledge the prospect’s views and respond with appropriate solutions. Take time to listen and understand what exactly may be giving them doubts.
- Ask questions. It will help shed more light on the matter, helping you find a solution quicker.
- Be ready with responses to your prospect’s objections. Even so, ensure you remain polite and courteous with your answers.
RELATED: Check out our tips on objection handling.
6. Closing the sale
This stage of the sales cycle can sometimes be challenging, but it doesn’t mean it’s impossible. Here, sales reps close the sale by asking powerful questions that move the prospect closer to the deal. If you play your cards right, the terms and deal finalization becomes an afterthought.
7. Follow up
Closing the deal doesn’t end there. Sales reps should follow up with their prospects as well as customers even after finalizing the sale. The goal is to make the customer a recurrent one, cementing their loyalty to your product or brand.
The process involves sending a thank you note or email and checking in with the client to see their progress and if the product met their expectations.
RELATED: Don’t forget to check out our powerful sales follow-up emails!
What is Sales Cycle Management?
Sales cycle management is keeping track of what happens during all of the sales life cycle stages, and adjusting to the buyer based on their behaviors during those key phases.
The sales cycle stages can vary greatly depending on mid-market vs enterprise, but they all stem from the process outlined below:
- Research-Discovery-Demo (RDD): A high-level demonstration with a conversation on the prospect’s role, business, and key initiatives.
- Custom Demo or POV: A deeper dive and working session to multiple stakeholders–establishes use cases and overall business impact from a practitioner and business leader’s perspective.
- Technical Win: The stage where we have established a technical fit within their marketing and sales ecosystem. The organization knows where we fit in and how we differentiate.
- Organizational Buy-In: Key stakeholders understand the impact for their business and the decision process, economic buyer, and champion are aligned on how our solution benefits their org.
- Contract Negotiation: All stakeholders involved understand the value and have an order form in hand–payment terms and price are negotiated at this point, if necessary.
- Closed-Won: =]
MEDDIC has traditionally been applied to Enterprise selling motions and acts to qualify complex B2B sales opportunities. Whether you’re selling high-volume/reduced ACV deals or whale-sized enterprise deals, you can leverage MEDDIC and Challenger Sales Methodology in your sales cycle management to proactively understand risk, leave your audience with actionable takeaways, and retain desirable sales cycle length.
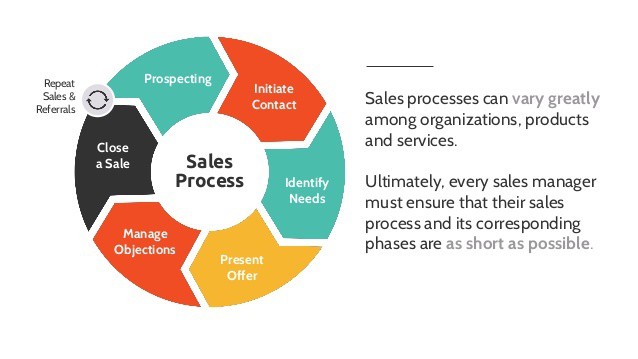
Image Credit: Daniel Nilsson
What Are the Elements of Sales Management?
There are three crucial elements in sales management:
- Sales Operation
- Sales Strategy
- Sales Analysis
Sales Operation and Team Building
This element of sales management involves identifying and bringing together efficient sales personnel from various divisions to form a sales team. It’s the sales manager’s role to ensure they delegate duties to the necessary people and make sure they are fulfilled.
A sales manager should gather as much information about the potential candidates of the sales teams so that every member is given the role they are best suited for. After assigning roles, sales managers then develop targets and goals for each member and ensure they accomplish them.
In addition to creating a sales team and assigning roles, sales managers are also responsible for keeping their team motivated and continuously evaluate them, offering feedback in the process.
Sales Strategy and Process
A sales manager has numerous roles within a business setting, and preparing a sales pipeline lies among the most important ones. A sales pipeline is a visual representation of a company’s sale process. It guides the sales teams and helps monitor and evaluate sales processes.
A sales pipeline also ensures members of the sales team stay organized and focused on their goals/targets.
Sales Analysis and Reporting
Sales analysis keeps sales teams on their toes by giving insight into areas where they need improvement and how to optimize specific strategies to get even higher returns.
Sales reporting involves the use of sales metrics to give more information on every aspect of your sales cycle as you monitor performance. These metrics include:
- Average deal size.
- The number of deals in your sales pipeline.
- Sales Velocity.
CRM tools are especially useful in this element of sales cycle management. They streamline sales operations, making management more effortless.
What’s MEDDIC?
- Metrics: How are your prospects measured…and what is the economic impact of your solution when mapped to their metrics?
- Economic Buyer(s): Who has the authority to sign off on a purchase?
- Decision Criteria: What does your solution or a similar offering need to have (features) and need to accomplish (value) to influence a purchasing decision?
- Decision Process: Functionally, who and how does a purchase happen in your prospect’s organization?
- Identification of Pain(s): Where does it hurt (emotional, rational, and economic) and is it linked to compelling events?
- Champion(s): Have you created a raging fan internally who can help influence and drive a win for both organizations?
If you’re able to understand your buyer’s unique situation and recognize MEDDIC during your initial discovery conversation—the likelihood of a streamlined sales opportunity dramatically skyrockets.
As Jacco vanderKooij critically highlights, please refrain from “selling” your solution before truly understanding how you and your solution helps your buyer:
“Prescription before diagnosis is malpractice.”
Your discovery calls should serve as active learning sessions for your prospects. With a mutual upfront contract, you and your buyer can both agree that the discussion will be mutually beneficial—so your conversation is relevant, tailored, and move to the next steps if both parties agree there is a fit.
The Challenger Methodology
Even without a full rollout of CEB’s Challenger program, you can leverage the fundamental takeaways from its methodology. When you weave in MEDDIC with Challenger, it becomes an immensely powerful process.
- Teach your buyers something new and actionable – Let them walk away with more than an understanding of your product. They should be able to understand how you differentiate amongst your competition. Show them how your solution can improve their “world of tomorrow.” Make them champions!
- Tailor your conversations and demos to be relevant – I promise that your pre-call research will help you have better sales conversations. Remember the metrics you learned? This is a great time to share how your solution can positively shape those very metrics with a solution like yours. Important business metrics apply to many personas in the same organization. Being relevant throughout your sales cycle management assures consensus among them.
- Take control of the conversations – Especially if they veer off the goal. It is your job to directly communicate insightful knowledge without coming off overly aggressive and off-putting. Remind your buyer of their decision criteria and reinforce what they shared with you during your last conversation.
Applying Sales Cycle Management Principles

Ask about their role… it’s okay to make concrete assumptions at this point, it allows you to ask specific questions about their sales metrics.
A few examples for Metrics: As the VP of Sales, I understand it’s top of mind for you and your reps to hit and exceed quota. What are some of the key initiatives you have in mind to drive higher attainment from your new hires?
Selling to an SDR Leader? They are typically measured by the following metrics:
- Sales Qualified Opportunities
- Meetings Booked/Occurred
- Percentage of Closed-Won Opportunities
Most often, it’s a mixture of all the above. You can dive into what conversion rates and concrete metrics they are looking to improve, and how your solution can help move the needle.
Economic Buyers & Your Champion: Identify who you are speaking with and what you need to do to gain ground with an Economic Buyer. Most decisions in today’s selling world require agreement from multiple stakeholders, even in the smallest of organizations.
It is vital you establish an internal champion who can assist in creating ground-swell to the decision makers. A champion can prove to be as helpful as a team member when it comes to sales cycle management. If you’re lucky, your Champion can also be your Economic Buyer!
Decision Criteria: This is ever elusive and is certainly the most difficult to extrapolate. You need to ask great questions to uncover the need-to-haves from the nice-to-haves. It is incredibly important to understand the “Why” behind some of their answers, as it gives clarity to both parties on what is a deal-breaker and what can be made as a concession.
Decision Process & Identification of Pain: Every sales org. should take enablement and coaching seriously—one of the first steps is to identify what questions to ask without it becoming an interrogation. Don’t forget, there are no excuses for a rep who doesn’t self-enable.
- Who else needs to see the solution to make an informed decision?
- How have you purchased a similar tool/solution/platform in the past?
- What does your process look like today and what feedback have you heard from your team?
- What are you currently doing to improve it?
The Challenger Methodology
Even without a full rollout of CEB’s Challenger program, you can leverage the fundamental takeaways from its methodology. When you weave in MEDDIC with Challenger, it becomes an immensely powerful process.
- Teach your buyers something new and actionable – Let them walk away with more than an understanding of your product. They should be able to understand how you differentiate amongst your competition. Show them how your solution can improve their “world of tomorrow”. Make them champions!
- Tailor your conversations and demos to be relevant—I promise that your pre-call research will help you have better sales conversations. Remember the metrics you learned? This is a great time to share how your solution can positively shape those very metrics with a solution like yours. Important business metrics apply to many personas in the same organization. Being relevant throughout your sales cycle management assures consensus among them.
- Take control of the conversations – Especially if they veer off goal. It is your job to directly communicate insightful knowledge without coming off overly aggressive and off putting. Remind your buyer of their decision criteria and reinforce what they shared with you during your last conversation.
Key Takeaways
Sales Cycle Management is the process of developing and establishing a sales team tasked with coordinating sales operations to allow businesses to meet their targets. It consists of three elements:
- Sales Operations: this is where the sales manager identifies suitable candidates and consolidates them into one sales team. It’s essential that sales managers keep their personnel motivated and ensure each team member is matched with a role they are best suited for.
- Sales Strategy: consists of formulating a sales pipeline where sales reps apply appropriate sales techniques to ensure optimal performance.
- Sales Analysis: involves the use of metrics to track company performance and identify areas that require improvement.
There are also three ways in which companies can apply sales cycle management principles, including:
1. Educating the prospects on the value of your product/service instead of selling it. By doing this, you set yourself apart from competitors by showing them what impact the solution you provide will bring.
2. Identify a Champion within your team who will help sell your product to prospects and help sales management.
3. Apply your findings from metrics into your demonstrations and presentations to make them more relevant and impactful on potential clients.